The financial sector is one of the most attacked industries in terms of cyber, due to the significant amount of data and sensitive assets it handles.
In recent years, the frequency and severity of cyber attacks on financial institutions have continued to increase, resulting in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory fines. In 2022 alone, more than 254 million personal files were leaked due to cyber breaches of financial institutions, and companies in the financial sector around the globe experienced more than 566 successful cyber attacks.
So what are the most common cyber threats to the financial sector, and how can organizations protect themselves against these threats?
Phishing
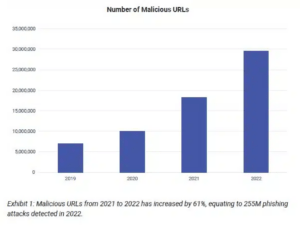
Phishing attacks remain one of the most common and effective cyber threats to the financial sector. These attacks are designed to trick people into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or financial data, by impersonating a trusted source or using social engineering tactics. In the financial sector, phishing attacks often target bank customers, employees, or managers in an attempt to gain access to their accounts or steal sensitive information.
To reduce the risk of phishing attacks, financial institutions should implement security awareness training programs for employees and customers, use multi-factor authentication, and deploy anti-phishing tools such as email filters and web filters.
Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks have become increasingly common in recent years, with financial institutions being a key target due to the potential for high financial gain – 66% of the organizations in the study were affected by ransomware in 2021, an increase from 37% in 2020.
In a ransom attack, hackers encrypt the organization’s data and demand payment in exchange for releasing the information. Ransomware attacks can cause significant financial losses, downtime, and damage to reputation. Common modes of operation of a ransomware virus are:
Encryption – software that locates files that seem important to the user – texts, documents, images, PDFs, and more. It encrypts the information, thus preventing access to it, but you will still be able to use your device. When a victim is a private person, the ransom usually amounts to several hundred dollars, and the requirement includes transferring the payment within 72 hours, otherwise, the information is permanently deleted.
Locking – in this case, the attack is relatively simple, the software locks the entire device, and the ransom note appears on the screen.